Learn about GraphQL Explorer features and user interface, including setup steps and the schema.
Square GraphQL Explorer is an interactive web application that lets you write, validate, and send queries for Square data. You can use GraphQL Explorer features (such as code completion, syntax validation, and on-page schema documentation) as you write queries and then run your queries against your own Square data. To access GraphQL Explorer, open https://developer.squareup.com/explorer/graphql and sign in to your Square account.
You can use GraphQL Explorer to:
Query the GraphQL endpoint in the Sandbox or production environment.
Browse the schema documentation to find available fields, type information, and query syntax.
Retrieve data for a single merchant using a personal or OAuth access token and filtering by the merchant's ID.
In a single query, you can retrieve data from one or more supported Square graphs, such as Orders, Catalog, Customers, and Payments.
Note
Square GraphQL supports query operations only. Mutations and subscriptions aren't supported. Queries are subject to rate and cost limiting.
After you set up GraphQL Explorer, you can enter queries in the left pane and run them to see real-time results against your Square data.
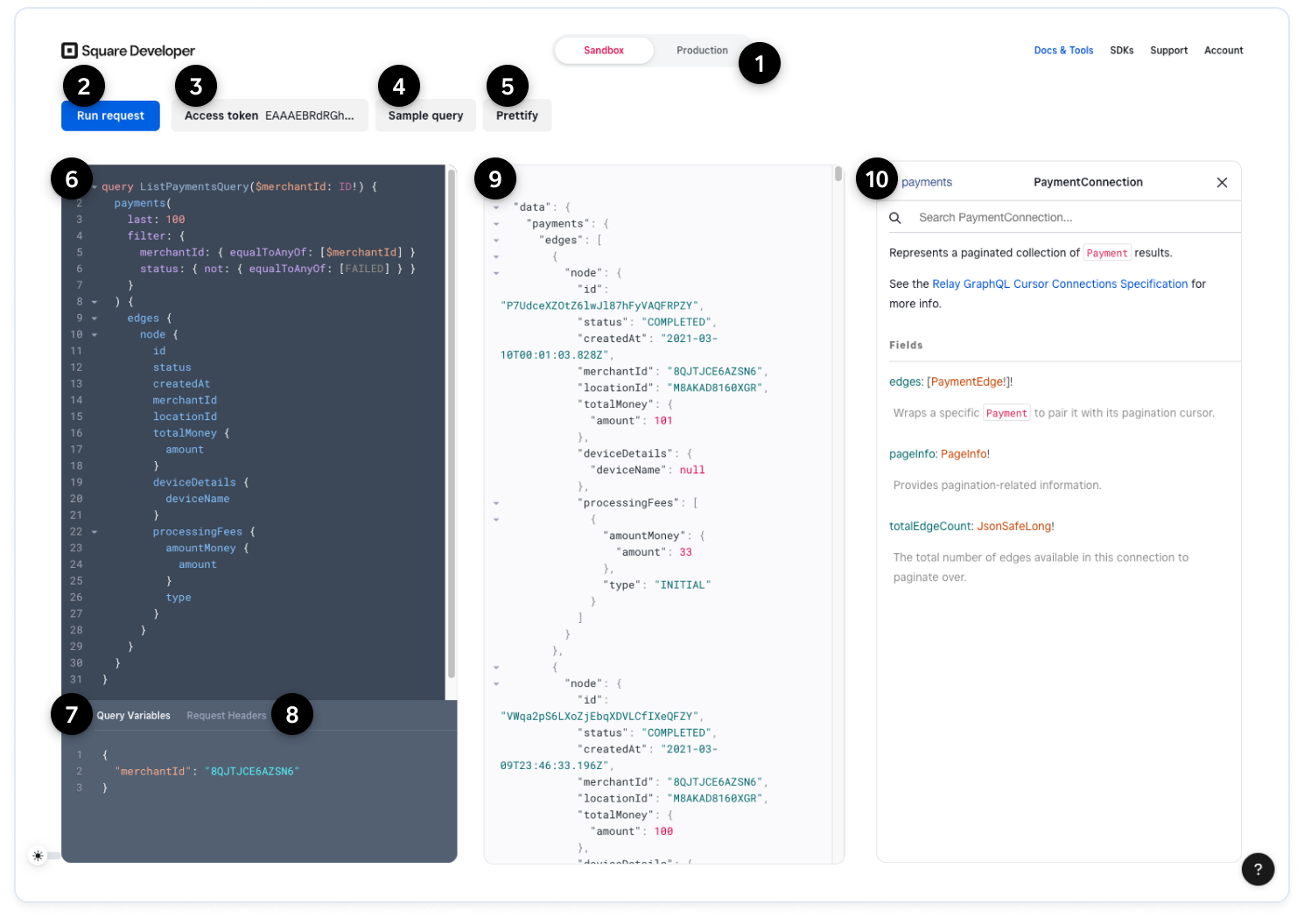
1. Sandbox or Production toggle
Lets you choose between the Sandbox or production environment. This selection determines whether GraphQL Explorer sends queries to the Sandbox endpoint or the production endpoint.
2. Run request button
Sends the current query and any query variables to Square GraphQL. Alternatively, you can use the Ctrl+Enter keyboard shortcut to send the query.
3. Add access token button
Lists the personal access tokens for the signed-in account. When you select an access token, it's added to the Request Headers pane and used for your queries. If you switch between Sandbox and production, you must reselect an access token that's valid for the environment. For more information, see Get set up to run queries.
To test a specific set of permissions, you can paste an OAuth access token into the Request Headers pane.
4. Sample query button
Lets you select a sample query to load into the query pane. Square provides a sample query for every graph entry point. All sample queries use query variables, so you need to enter valid values into the Query Variables pane before running the query.
5. Prettify button
Applies proper spacing and indentation and removes comments and extra line breaks.
6. Query pane
Lets you enter and edit queries and provides code completion, code hints, and syntax and schema highlighting and validation. For code completion, you can begin typing or use Ctrl+Space to show suggestions.
7. Query Variables pane
Stores the variables used in the query and their values. Using variables in queries is optional, but all sample queries use them. For more information, see Variables.
8. Request Headers pane
Stores the request headers for the query. All queries require an Authorization header and bearer access token. If you want to test OAuth permissions, paste the OAuth access token directly into this pane.
You can include "x-graphql-include-debug": 1 in the request headers to return an extensions object with debugging information. Currently, this object contains the query's complexity score and a request ID that you can provide to Square support.
9. Results pane
Shows real-time responses with results and error information for the queries you run.
10. Documentation Explorer
Provides searchable schema documentation. If this pane is hidden, open it using the Docs button. For more information, see Browse the schema documentation.
In addition, you can toggle between light and dark mode or leave feedback using the controls at the bottom of the page.