Applies to: Catalog API
Learn how to add custom attributes to your catalog objects and delete custom attribute definitions.
Custom attributes can be used to associate additional information with supported catalog objects. For example, a quick service restaurant uses an order-ahead application from a partner developer. The application needs additional information for each menu item:
- An application-specific menu item name, such as "Chicken" instead of the original item name of "CHK".
- An application-specific price.
- Allergen information.
Because catalog items don't have properties for this information, the seller can have custom attributes added to a CatalogItem object in their catalog to capture the additional details.
The following catalog object types can accept custom attributes:
ITEM- Attributes are visible in the Square Dashboard and the API.ITEM_VARIATION- Attributes are visible in the Square Dashboard and the API.MODIFIER(2023-04-19 or later) - Attributes are visible only with the API.MODIFIER_LIST(2024-04-17 or later) - Attributes are visible only with the API.CATEGORY(2024-04-17 or later) - Attributes are visible only with the API.
Important
The Square Point of Sale application doesn't show custom attributes for any object type.
- Each Square account can have up to 10 seller-visible and 10 seller-hidden custom attributes.
- You cannot edit the
source_application,type,key,max_allowed_selections, orallowed_object_typesof a custom attribute after creation. - You cannot edit the configuration for
STRINGtype attributes after creation. - Custom attributes are available for Square version 2020-03-25 or later.
A catalog custom attribute has two parts: a definition and a set of values that can be empty. A value can be saved after the definition is set for supported object types. After a custom attribute definition is set to be applicable to an object, such as a CatalogItem or CatalogItemVariation, that definition is available for all objects of that type.
In the Square Dashboard, the seller edits an item to input a custom attribute value. A seller sees placeholders for all available definitions in every supported object even if values haven't yet been assigned.
Suppose a seller creates the following custom attribute definitions and allows them for items and item variations unless otherwise noted:
- Brand
- Components Brand
- Filling types
- Helmet Brand
- Shoe Brand
- Shoelace types - item variation only
- Tasting Notes
- Tea Brand
Because most of the definitions can be set on items and item variations, they appear on every item and item variation in the seller's catalog.
The following image from the Square Dashboard shows a shoelace item variation with a selected value for "Shoelace types" and no values for any other custom attributes.
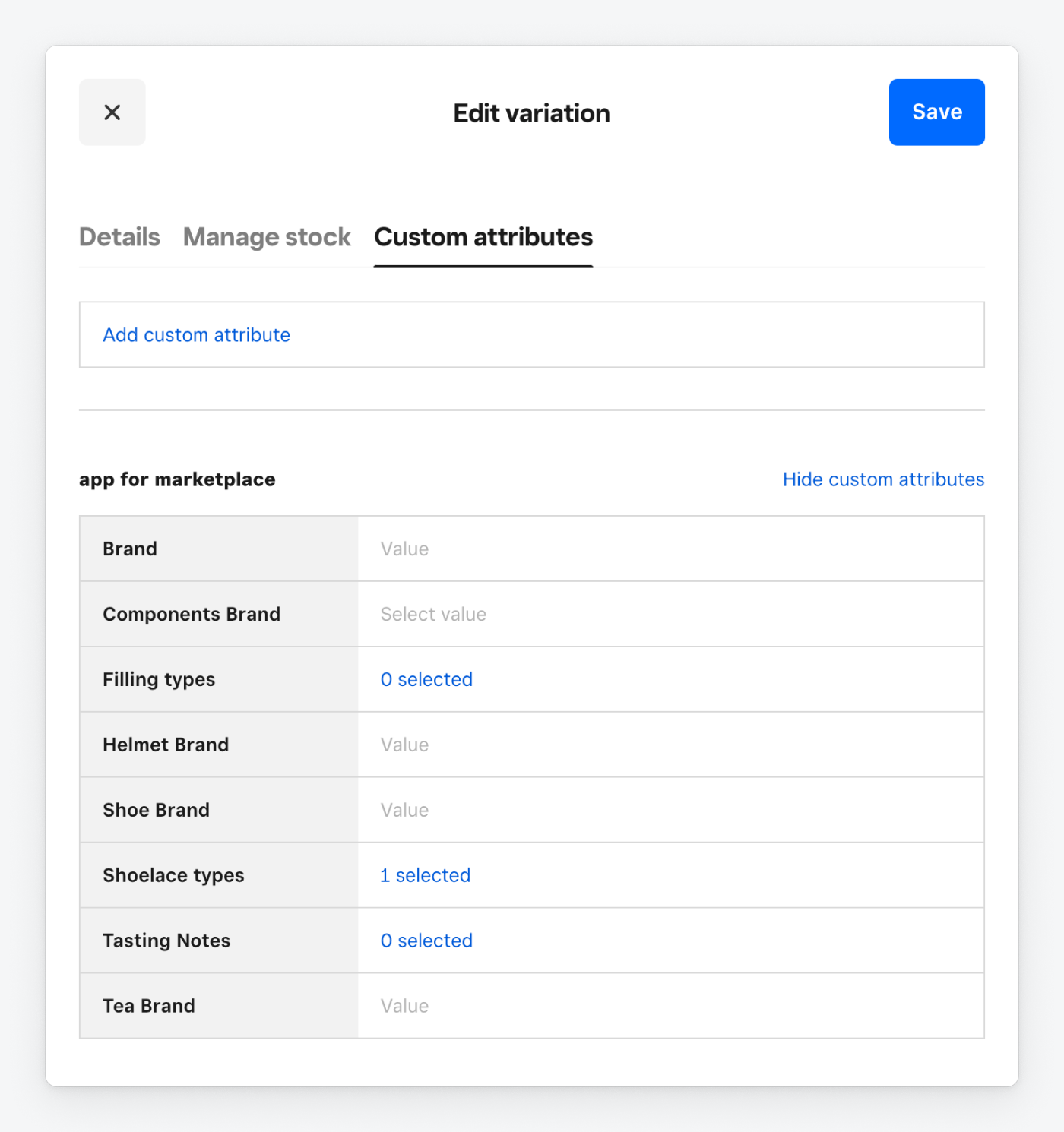
The CatalogItemVariation for the shoelaces has a custom_attribute_values property like the following example:
The following example creates a new item variation for shoelaces. The variation is an 8" lace with a custom attribute set for the first of two possible values defined for shoelace types.
curl https://connect.squareupsandbox.com/v2/catalog/object \ -X POST \ -H 'Square-Version: 2025-02-20' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer {YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "idempotency_key": "f1c31066-7b94-4d32-90a6-12a4398f1406", "object": { "type": "ITEM_VARIATION", "id": "HXSNEZN7N3NBGJX2XJ2Z6R5Q", "updated_at": "2025-02-19T23:20:25.835Z", "created_at": "2024-08-29T17:34:20.395Z", "version": 1740007225835, "is_deleted": false, "custom_attribute_values": { "Shoelace_Types": { "name": "Shoelace types", "custom_attribute_definition_id": "RLBNUGHJ3CVQXXUV37VMFYZW", "type": "SELECTION", "selection_uid_values": [ "INYXXB6WEZVCPM3AMD343LY2" ], "key": "Shoelace_Types" } }, "present_at_all_locations": true, "item_variation_data": { "item_id": "QWNIQEIK4VSPPQHEKZOZ4EYJ", "name": "8'' laces", "ordinal": 1, "pricing_type": "FIXED_PRICING", "price_money": { "amount": 234, "currency": "USD" }, "location_overrides": [ { "location_id": "E78VDDVFW1EYX", "track_inventory": false }, { "location_id": "LFF3HK0DN6A61", "track_inventory": false } ], "track_inventory": false, "measurement_unit_id": "QTSYO4OCO6RIV2UWZOP6BRLV", "sellable": true, "stockable": true } } }'
Note that the item doesn't show custom attributes for the definitions that don't have values.
The custom_attribute_values property of a catalog object is a key/value pair, allowing you to add an attribute value for each custom attribute you define. For example, you might add custom attributes to a bicycle item variation. Modifiers like size and color should be buyer-selectable and visible at the point of sale. You might also associate the brand of a component group by creating custom attribute definitions for the component brand and ID.
{ "custom_attribute_values": { "component_brand": { "key": "component_brand", "custom_attribute_definition_id": "IQN73SQGHTOWP4JKZQNQDSKB", "name": "Brand", "type": "STRING", "string_value": "Shimano" } } }
Because custom_attribute_values is a map, you need to define a map key, such as component_brand. This key string should match the key assigned to the custom attribute definition. Additionally, set the key field in the map object to the same string as the map key.
An application can create up to 10 seller-visible custom attribute definitions defined by a CatalogCustomAttributeDefinition object. Custom attribute definitions appear on the Edit Item page in the Square Dashboard, where people with sufficient permissions can see and edit the custom attribute values.
You can control whether a seller or another application can see your custom attribute values applied to catalog items by setting the CatalogCustomAttributeDefinition app_visibility and seller_visibility fields.
Note that the application that created a custom attribute definition always has the ability to retrieve, search, and update the values of any custom attribute that uses that definition.
The app_visibility field controls whether the custom attribute and its definition are readable or writable by other applications:
APP_VISIBILITY_READ_ONLY- The attribute definition and value are read-only, visible, and searchable by other applications.APP_VISIBILITY_READ_WRITE_VALUES- The attribute definition and value are read-write for other applications.APP_VISIBILITY_HIDDEN- The attribute definition and its attribute values aren't visible to other applications.
The seller_visibility field controls whether the custom attribute definition and value appear in the UI of Square products, such as the Square Point of Sale application or the Square Dashboard:
SELLER_VISIBILITY_READ_WRITE_VALUES- Sellers can search for and edit the custom attribute. For example, an application can set a custom attribute definition withseller_visibilityset toSELLER_VISIBILITY_READ_WRITE_VALUES. This allows sellers to read and write the custom attribute values from the Square Dashboard. Sellers can also search for this custom attribute, which is useful for storing important data.SELLER_VISIBILITY_HIDDEN- Sellers cannot see custom attribute definitions or the associated values.
In the following example, the item library shows two custom attribute definitions created in the Square Dashboard and two created with the Catalog API. The custom attributes created with the Catalog API show the creating applications in parentheses because they were created with seller_visibility set to SELLER_VISIBILITY_READ_WRITE_VALUES.
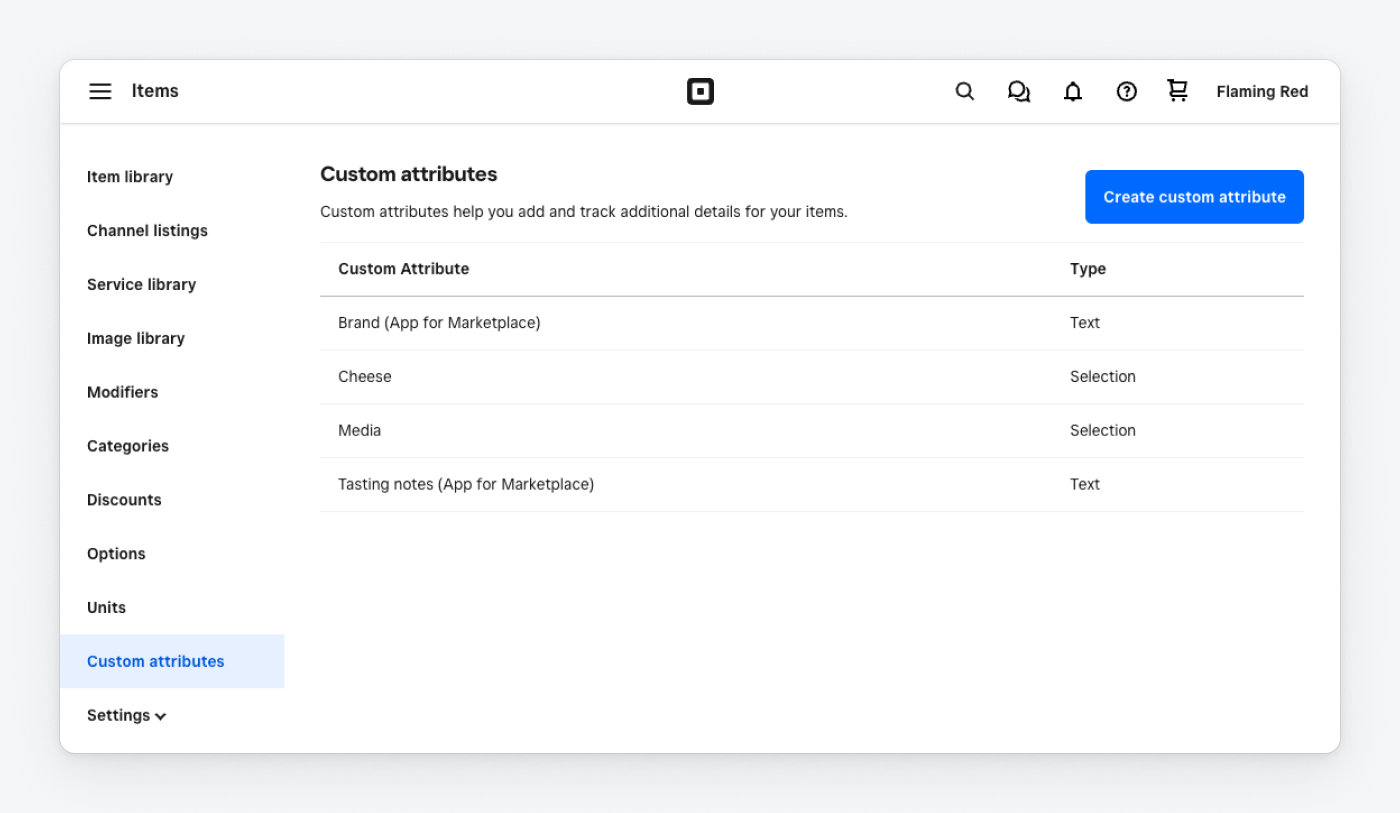
Any custom attribute definition that's visible in the custom attribute definition list can also be added to a catalog item, variation, modifier list, or category.
A custom attribute can be of one of the following types:
- Selection - A set of up to 100 value strings that a seller can input and then choose from.
- String - A free-form string input by the seller.
- Number - A five digit number input by the seller.
- Boolean - A true or false value selected by the seller.
A SELECTION type custom attribute has multiple selectable values defined by the developer in the CatalogCustomAttributeDefinitionSelectionConfig object. SELECTION type attributes can also allow single or multiple value selections. You can predefine up to 100 choice value properties and each item can have up to 100 of these choices active at any time.
For example, a restaurant seller might create a custom attribute for cheese to apply to all menu items with cheese. They can list every type of cheese and activate specific ones like "Cheddar" and "Pepper Jack" for hamburgers and "American Cheese" and "Munster" for macaroni and cheese, leaving out others like "Gouda".
A STRING type custom attribute can take any free-form string value of up to 255 characters. The string value can include any Unicode character code. Empty strings are also allowed.
Each custom attribute with the NUMBER type can store values with up to 5 decimal places and can support values up to approximately 90 trillion (exact value 263/100,000).
A true or false value. For example, BOOLEAN type custom attributes can be used to set whether an item is available for delivery in a third-party delivery application.
To use custom attributes, you need to:
- Create a CatalogCustomAttributeDefinition, define a
CatalogObjectwith the typeCUSTOM_ATTRIBUTE_DEFINITIONand assign the relevant data to thecustom_attribute_definition_dataobject. This data should include the attribute type and the allowed hosting object types.Did you know?
You don't need to set the
app_visibilityandseller_visibilityif you want to use the default values ofSELLER_VISIBILITY_READ_WRITE_VALUESandAPP_VISIBILITY_HIDDEN. - Accept seller input and assign that value to the custom attribute on a specified hosting catalog item, item variation, or modifier.
In the following example, custom attributes are created to help a seller keep track of the brand of cocoa and type of topping for a Hot Cocoa item. These attributes use STRING and SELECTION values. The key you choose in the definition becomes the name of the attribute in the catalog item. For example, if you use the key "cocoa_brand", the catalog item needs to have a custom_attribute_values.cocoa_brand object to store the attribute values.
The example also includes a custom attribute definition from another application. The custom_attribute_values.a-different-application_id:ingredients object refers to that definition and provides a string value.
curl https://connect.squareupsandbox.com/v2/catalog/batch-upsert \ -X POST \ -H 'Square-Version: 2025-02-20' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer {YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "idempotency_key": "sdsd-4876-b3cf-3sexy332", "batches": [ { "objects": [ { "id": "#tea_brand", "type": "CUSTOM_ATTRIBUTE_DEFINITION", "custom_attribute_definition_data": { "allowed_object_types": [ "ITEM", "ITEM_VARIATION" ], "name": "Tea Brand", "type": "STRING", "key": "tea_brand" } }, { "id": "#filling", "type": "CUSTOM_ATTRIBUTE_DEFINITION", "custom_attribute_definition_data": { "allowed_object_types": [ "ITEM", "ITEM_VARIATION" ], "name": "Filling types", "type": "SELECTION", "key": "filling", "selection_config": { "allowed_selections": [ { "name": "Marshmallow", "uid": "#marshmallow" }, { "name": "Whipped Cream", "uid": "#whipped_cream" } ], "max_allowed_selections": 2 } } }, { "id": "#hot-tea", "type": "ITEM", "custom_attribute_values": { "tea_brand": { "key": "tea_brand", "custom_attribute_definition_id": "#tea_brand", "name": "Brand", "type": "STRING", "string_value": "Tea Magic" }, "Filling": { "key": "Filling", "custom_attribute_definition_id": "#filling", "name": "Filling", "type": "SELECTION", "selection_uid_values": [ "#marshmallow", "#whipped_cream" ] } }, "item_data": { "name": "Hot Tea", "variations": [ { "id": "#hot-tea-small", "type": "ITEM_VARIATION", "item_variation_data": { "name": "Small", "pricing_type": "FIXED_PRICING", "price_money": { "amount": 500, "currency": "USD" } } } ] } } ] } ] }'
Note
You need to specify the allowed_object_types for your new custom attribute definitions to be displayed in the Square Dashboard. You cannot change the list of allowed object types after you've set it in your create request.
In the previous example, the custom_attribute_values field includes "custom_attribute_definition_id": "#cocoa_brand". When you're creating a batch-upsert request, be sure to include this field when you use the custom_attribute_values field.
An application can change which custom attribute definition a catalog object references, regardless of who created the definition. To prevent your custom attribute definitions from being removed, set their visibility to APP_VISIBILITY_READ_ONLY.
The custom attribute definition that you intend to delete might be referenced by a catalog object. You should get these catalog objects and update them to clear their custom attribute values and reference to the custom attribute definition that you're deleting.
To delete a custom attribute definition from the catalog, call the DeleteCatalogObject endpoint while supplying the custom attribute definition ID as the object_id path parameter value. In the following example, the custom attribute definition object ID is assumed to be VEER7NOZJRW75LXVVVS4BX25:
Delete catalog object