Learn about error responses and best practices for error handling and logging.
Square APIs always return a response. If a request succeeds, the response includes a header with an HTTP status code of 200. If a request fails, the response includes a header with a status code ranging from 400 to 599.
Error responses include an errors array with an Error object for each error that occurred while processing the request. If multiple errors are returned, the status code matches the first one. Depending on how the request is processed, it's possible to receive a subsequent error response after fixing and retrying a request.
Bulk endpoints are an exception; they might also return errors for individual operations within a 200 response.
The Error object provides error information using the following properties:
category- A high-level classification of the error. For a complete list of category values, see ErrorCategory.code- A specific identifier for the error. For a complete list of error codes, see ErrorCode.detail- A human-readable error description for developers, not intended to be customer facing. This is an optional error field.field- The name of the field in the original request (if applicable) that the error pertains to. This is an optional error field.
The following example requests return an error response:
GetPayment using a nonexistent payment ID
Get payment
UpdateCustomer using invalid values
Update customer
Avoid presenting a raw Error object directly to the user. Instead, your code should anticipate common errors and respond with user-friendly messages. The overall tone of these messages should be similar to other messages that your application shows to users. Direct users to contact your own support team (instead of Square support) about any questions or issues that arise when using your application.
Your application should respond gracefully to errors. Some common techniques include the following:
Catch and handle errors so that the application doesn't crash or freeze. Use try-catch blocks or similar mechanisms to handle exceptions and determine next steps.
If an API call fails, consider providing a fallback option or alternative approach. This can help users perform their tasks even if an API is temporarily unavailable.
Set up a continuous monitoring mechanism for the application to collect information about errors and report them. This can help identify recurring issues and allow developers to proactively address them.
Write errors to an error log so developers can diagnose and fix issues. This can include logging relevant information such as error type, stack trace, user context, and any other useful details.
Did you know?
Square provides an API Logs feature that captures data about your API calls. You can use the log data for diagnostics, troubleshooting, and auditing.
The Square SDKs provide language-specific error-handling mechanisms that you can use in your code. For more information and code snippets, see the quickstart guide:
If you receive an AUTHENTICATION_ERROR error with a 401 Unauthorized status, the access token used in the API request is probably invalid.
{ "errors": [ { "category": "AUTHENTICATION_ERROR", "code": "UNAUTHORIZED", "detail": "This request could not be authorized." } ] }
During development, these UNAUTHORIZED errors are commonly encountered when switching between the production and Sandbox environments. To troubleshoot, first make sure you're using the correct access token for the target environment:
- If needed, find the access token and target environment in the failing request. For more information, see Use an access token in your code.
- Use the access token to call RetrieveTokenStatus in the production or Sandbox environment. A valid token returns a
200 OKresponse and ascopesarray that lists the authorized permissions.
Note
When testing with a personal access token for your own Square account, you can check whether you're using the correct one in the Developer Console. Open your application, toggle to Sandbox or Production, and then view the token on the Credentials page.
Other issues might result in AUTHENTICATION_ERROR errors. For example:
- The provided access token is expired or revoked, or you're sending the encrypted value.
- The provided access token doesn't grant sufficient permissions to use the API endpoint you're calling.
- The
Authenticationheader isn't properly formatted with a bearer token or the access token is missing from the request. - The application ID and secret you provided in the ObtainToken request is from the wrong (production or Sandbox) environment.
- You didn't remove
{ },< >, or other placeholder characters that you copied from a code example.
Make sure to handle these issues in your implementation. For example, test with specific OAuth permissions, regularly refresh access tokens, and listen for oauth.authorization.revoked events. For more information, see OAuth Best Practices and Move OAuth from the Sandbox to Production.
Errors in the AUTHENTICATION_ERROR category return a 401 or 403 status code with one of the error codes shown in the following table:
| Status | ErrorCode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | UNAUTHORIZED | A general authorization error occurred. |
| 401 | ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRED | The access token provided in the request recently expired. |
| 401 | ACCESS_TOKEN_REVOKED | The access token provided in the request was revoked. The revoker_type field in the oauth.authorization.revoked event payload indicates the type of client that revoked the token: APPLICATION, MERCHANT, or SQUARE. |
| 401 | CLIENT_DISABLED | The provided client has been disabled. |
| 403 | FORBIDDEN | A general access error occurred. |
| 403 | INSUFFICIENT_SCOPES | The access token provided in the request doesn't have sufficient permissions to perform the requested action. |
Note
Some INVALID_REQUEST_ERROR errors also return a 403 status code, so make sure to check the ErrorCode type.
If your application sends a high number of requests to Square APIs in a short period of time, Square might temporarily stop processing your requests and return RATE_LIMITED errors with a 429 Too Many Requests status.
When this occurs, the API Logs page in the Developer Console displays errors with a 429 status code.
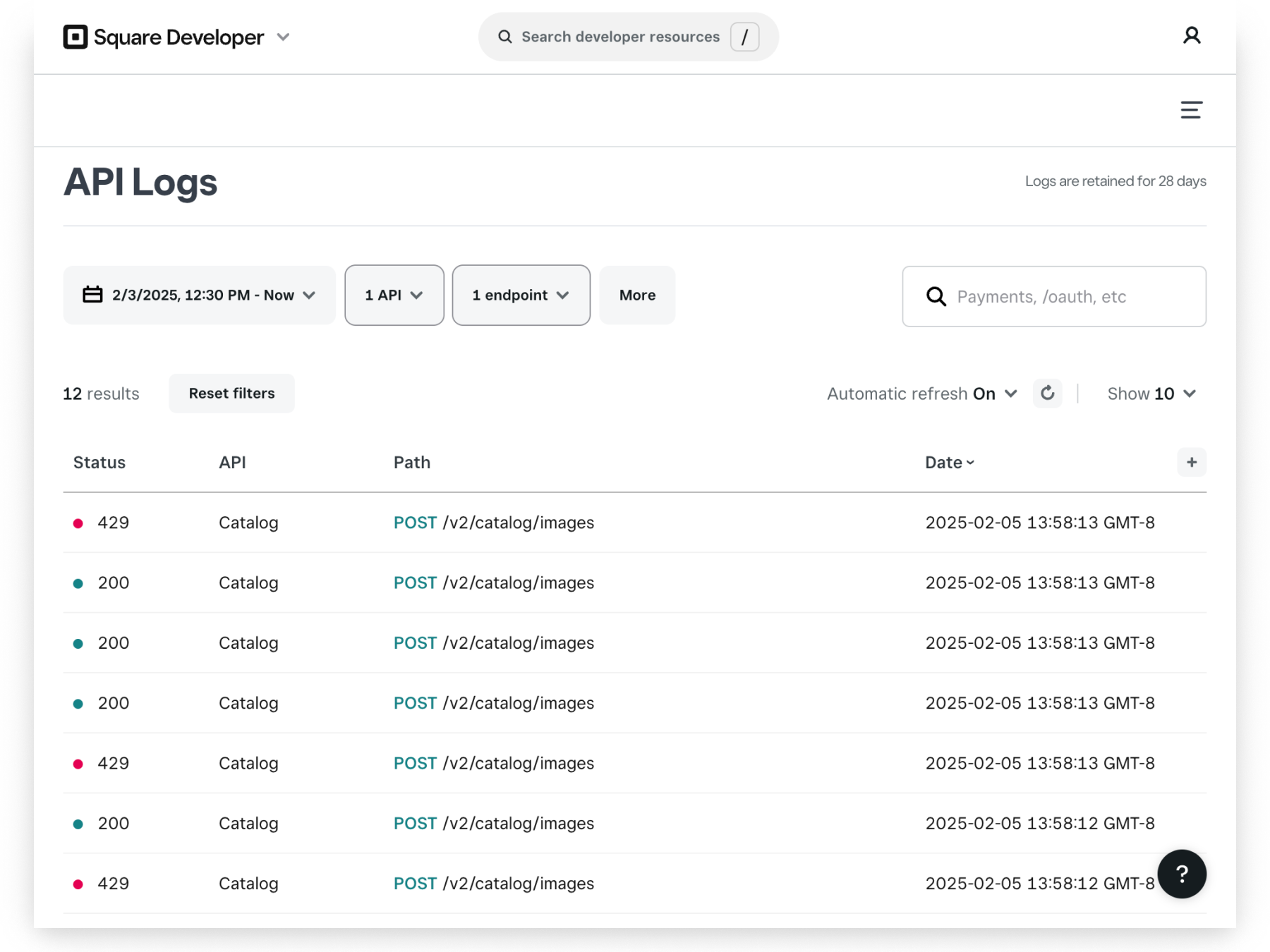
Your application should monitor responses for 429 errors and use a retry mechanism with an exponential backoff schedule to resend the requests at an increasingly slower rate. It's also a good practice to use a randomized delay (jitter) in your retry schedule to avoid a thundering herd effect.
Note
To comply with App Marketplace requirements, applications must watch for 429 errors and retry requests using exponential backoff.
Square API endpoints might enforce different rate limits. Logging data about error rates can help identify which API calls in your code encounter 429 errors, so you can make changes to avoid or handle rate limiting errors. For example:
Use
BatchandBulkendpoints when available. These endpoints allow you to perform multiple operations in a single request.Use available filters with
SearchandListendpoints to limit your requests to the data you need.Integrate existing libraries or mechanisms that can handle rate limiting for you in your code.
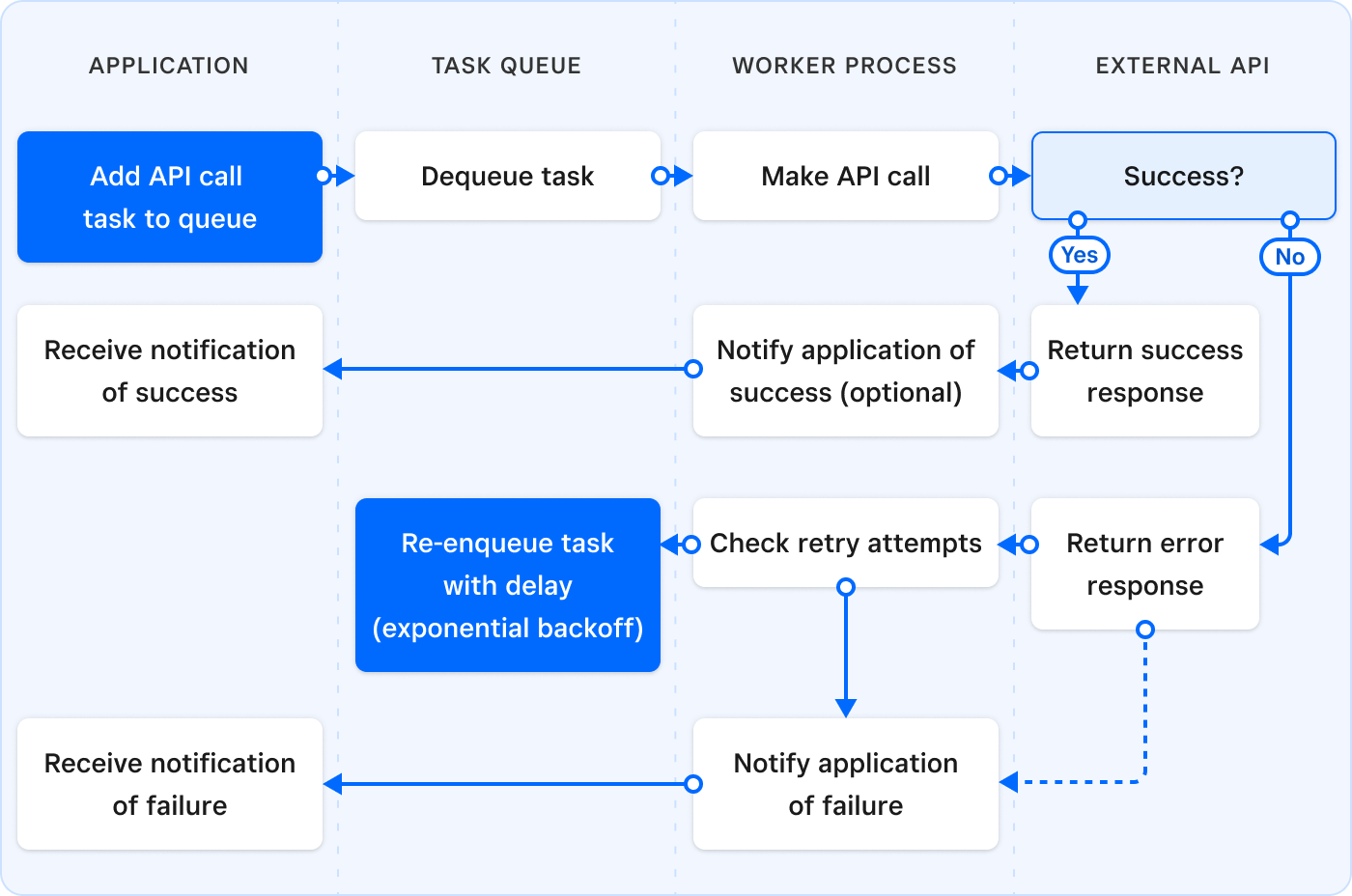
Implement a worker queue system to manage API calls. This system allows you to centrally control your call frequency and retry logic. It's particularly useful for API calls that are prone to rate limiting, but can also improve reliability for high-volume API calls and critical operations.
A worker queue system uses the following high-level steps:
- When an API call needs to be made, the task is added to a queue instead of being executed immediately.
- A worker picks the task from the queue and executes the API call.
- If the worker receives a
429rate limit error, it adds the task back into the queue to be retried later. Note that:- You should retry calls with increasing intervals (for example, by using exponential backoff and randomized delay).
- You should log this activity for future analysis.
Note
- For information about preventing rate limiting with catalog operations, see Synchronize a Catalog with an External Platform.
- GraphQL queries are also subject to rate limiting. For more information, see Rate limiting for Square GraphQL.